NullSender - Modern Phishing Chains and Tunneling
Explore how modern attackers use Cloudflare Tunnels and multi-stage payload delivery to evade detection and create highly effective social engineering campaigns.
Executive Summary
NullSender is designed to help red teamers and security researchers simulate modern phishing campaigns that abuse Cloudflare Tunnels. Remote Access Trojans (RATs) including AsyncRAT, Xworm, and VenomRAT have been observed abusing trycloudflare, an anonymous and secure Cloudflare tunnel service that requires no registration or payment.
Campaigns observed between mid-2024 and mid-2025 have used shortcut files (.LNK), WebDAV servers, and living-off-the-land (LoL) binaries like robocopy, cscript, and mshta to deliver and execute payloads. The newly observed SERPENTINE#CLOUD campaign continues this pattern, introducing slight variations in delivery and staging techniques while maintaining the core abuse of Cloudflare's infrastructure.
NullSender automates the setup of "staged" payloads hosted over WebDAV and generates deceptive .lnk shortcuts that appear legitimate, masquerading as legitimate PDF documents.
Motivation: Abuse of Cloudflare Tunnels in the Wild
Since mid-2024, security researchers at eSentire and Proofpoint have documented a significant wave of malware campaigns abusing Cloudflare tunnels (via trycloudflare[.]com) for anonymous, secure staging and delivery of malware. Comprehensive analyses have highlighted how multiple malware families leverage trycloudflare[.]com URLs to host multi-stage attack chains while evading traditional network security controls.

Figure 1 - Frequency of trycloudflare usage in malware campaigns
Using the Cloudflared CLI tool, adversaries can spin up a secure tunnel from their local environment and expose internal services (such as a local WebDAV server) to the internet — without requiring a public IP address, domain registration, or complex port forwarding. An example of a generated tunnel URL might be:
flour-riding-merit-refers.trycloudflare[.]comThese automatically generated domains typically host malicious payloads or serve as staging areas for multi-stage attacks via protocols like WebDAV or HTTP. They're frequently coupled with living-off-the-land binaries (LoLBins) such as curl, bitsadmin, or robocopy. The tunnel's inherent anonymity, built-in encryption, and ease of deployment make it an increasingly attractive attack vector for malware campaigns seeking to evade network detection systems and traditional perimeter defenses.
May 2024 Campaign
Security researchers at eSentire first documented attackers systematically using Cloudflare Tunnels to deliver malware in May 2024 (initially reported in July). In this foundational campaign, victims received ZIP archives containing malicious .URL files, which redirected to .LNK shortcut files hosted behind Cloudflare Tunnels.
The .LNK files, when executed by unsuspecting users, triggered download chains that retrieved additional malware components from local WebDAV servers that had been exposed to the internet via trycloudflare[.]com. This approach demonstrated a novel delivery vector where all attack infrastructure could remain completely local and anonymous, avoiding traditional domain attribution challenges.
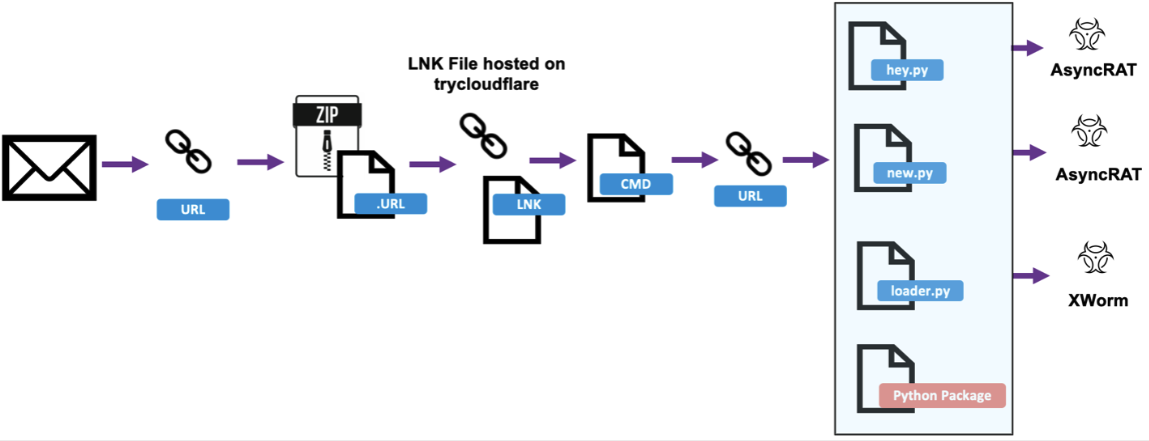
Figure 2 - May 2024 attack chain flow
July 2024 Campaign
Attackers shifted their tactics to deploy HTML files that triggered the search-ms protocol, which pointed to Cloudflare-hosted shortcut payloads disguised as legitimate documents. These payloads continued to leverage tunneled WebDAV servers and simple Python HTTP servers to deliver subsequent-stage scripts and executables.
The increase in delivery method variations indicated increasingly more mature phishing infrastructure development and a growing reliance on advanced social engineering techniques to achieve initial code execution on target systems.
Figure 3 - July 2024 attack chain flow with search-ms:query abuse
June 2025 SERPENTINE#CLOUD Campaign
The most recent and sophisticated evolution appeared in June 2025 with the SERPENTINE#CLOUD campaign, comprehensively documented by Securonix researchers. This campaign significantly refined the attack chain, using carefully crafted .LNK files disguised as PDF documents to download Windows Script Files (.WSF) via Cloudflare-exposed WebDAV servers.
Once executed, the .WSF scripts launched heavily obfuscated batch files, which subsequently decoded and executed packed Python loaders designed to deploy AsyncRAT or RevengeRAT remote access trojans. Despite multiple obfuscation layers, the campaign still maintained its reliance on Cloudflare Tunnels, deceptive shortcuts, and multi-stage scripting approaches.
SERPENTINE#CLOUD represents the current state-of-the-art for this attack methodology, incorporating lessons learned from previous campaigns while adding significant defensive evasion capabilities.
Why This Inspired NullSender
The consistent and evolving use of Cloudflare Tunnels across these campaigns represents more than a temporary trend — it reflects how genuinely accessible and operationally powerful this tunneling infrastructure has become for threat actors. Cloudflare Tunnels provide a unique combination of stealth, operational flexibility, and ease of deployment that's difficult to replicate with traditional attack infrastructure.
This persistent abuse pattern served as the primary motivation behind NullSender's creation, as security professionals needed a way to safely replicate and understand these techniques.
From an attacker's perspective, Cloudflare Tunnels offer several strategic advantages:
These operational properties closely mirror those of professional red team infrastructure, but with zero financial cost and dramatically reduced technical complexity — creating a dangerous combination when leveraged by malicious actors.
Introducing NullSender
NullSender was specifically designed to emulate these real-world attack structures in a controlled, repeatable, and highly customizable manner. The tool enables red teamers, threat intelligence analysts, and security educators to accurately replicate these evolving tactics — from initial tunnel creation through complete multi-stage payload delivery — using only PowerShell and widely available system components.
By precisely mirroring the operational structure of active threat campaigns, NullSender provides security professionals with the capability to understand, simulate, detect, and ultimately defend against the techniques that threat actors are continuously refining in production environments.
What NullSender Does
NullSender automates the full setup of a Cloudflare-based phishing campaign, including:
- Generating realistic .lnk files disguised as PDFs.
- Setting up an IIS WebDAV server to host your malicious payloads.
- Starting a Cloudflare Tunnel to make the server externally reachable.
- Creating multi-stage payload chains using .WSF and .BAT scripts.
- Embedding custom icons, filenames, and descriptions into payloads.
Use Cases
NullSender is designed for:
- Red teams simulating real-world malware TTPs.
- Malware analysts testing detection logic.
- Threat educators demonstrating Cloudflare Tunnel abuse.
- Blue teams hardening detection for trycloudflare[.]com-based C2.
References
- • eSentire - Quartet of Trouble: XWorm, AsyncRAT, VenomRAT, and PureLogs
- • Proofpoint - Threat Actor Abuses Cloudflare Tunnels to Deliver RATs
- • Sean Ferguson - Analyzing SERPENTINE#CLOUD: Threat Actors Abuse Cloudflare
- • Forcepoint - AsyncRAT Reloaded: Using Python and TryCloudflare for Malware
- • Broadcom - AsyncRAT malware campaign using Cloudflare Tunnel